Introduction
Imagine finding exactly what you need on Google in seconds instead of scrolling through pages of irrelevant results. That’s the power of Google search operators – specialized commands that transform your basic searches into precision tools.
Whether you’re a digital marketer tracking competitor mentions, an SEO professional analyzing backlinks, or a business owner researching your industry, mastering these operators can save you hours of manual searching. Google Search operators stand as powerful tools that can refine your search results precisely to your needs, and in this guide, you’ll learn exactly how to use them.
In the next 10 minutes, you’ll discover 40+ working search operators, practical use cases for each, and real-world examples that you can implement immediately.
What Are Google Search Operators?
Google search operators are special commands and symbols that you add to your search queries to get more specific and targeted results. Think of them as advanced filters that tell Google exactly what type of information you’re looking for.
Google search operators help narrow down results and find more relevant information by directing Google to focus on specific webpage aspects. Instead of searching through hundreds of general results, these operators help you find:
- Specific file types (PDFs, presentations, spreadsheets)
- Content from particular websites or domains
- Exact phrases and quotes
- Pages published within certain timeframes
- Technical website information for SEO analysis
Why Search Operators Matter in 2025
Google is still the undisputed king of Search Engines. (89.79% worldwide market share as of January 2025.) With billions of web pages indexed, finding precise information without operators is like searching for a needle in a haystack.
For professionals, these operators provide competitive intelligence, content research capabilities, and technical SEO insights that would otherwise require expensive tools.
Essential Google Search Operators Every User Should Know

Basic Text Operators
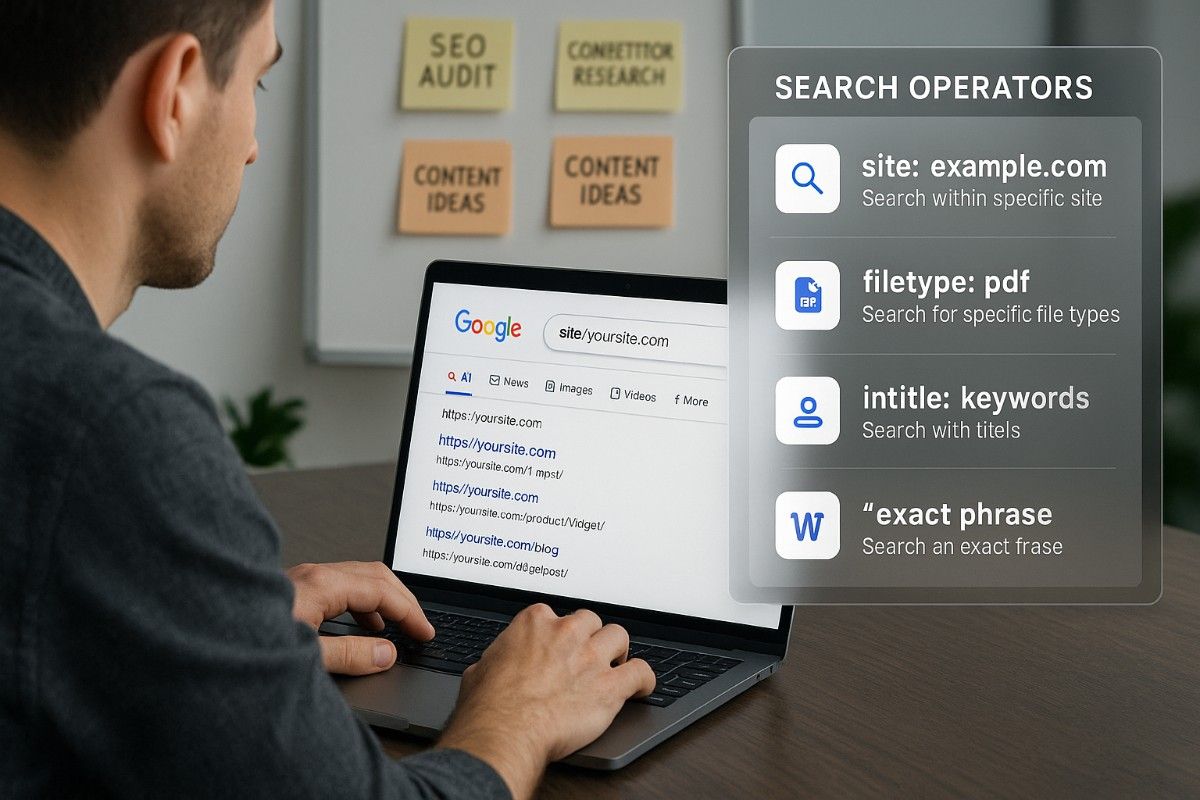
1. Double Quotes (” “)
Purpose: Find exact phrases Syntax: "your exact phrase" Example: "digital marketing strategy" returns only pages containing this exact phrase Use Case: Research competitor messaging or find specific quotes
2. Minus Sign (-)
Purpose: Exclude specific terms Syntax: search term -excluded word Example: marketing strategies -social finds marketing content excluding social media Use Case: Remove irrelevant results from broad searches
3. Plus Sign (+) or OR
Purpose: Include either/both terms Syntax: term1 OR term2 or term1 + term2 Example: "content marketing" OR "inbound marketing" Use Case: Research related topics or synonyms
4. Wildcard (*)
Purpose: Replace unknown words in phrases Syntax: "phrase with * word" Example: "best * marketing tools" finds “best email marketing tools,” “best social marketing tools,” etc. Use Case: Discover related phrases and long-tail keywords
Website-Specific Operators
5. Site: Operator
Purpose: Search within specific websites Syntax: site:domain.com search terms Example: site:salesnanny.com SEO finds all SEO-related content on SalesNanny Use Case: Audit your own content or analyze competitor websites
6. Related: Operator
Purpose: Find similar websites Syntax: related:domain.com Example: related:hubspot.com discovers marketing platforms similar to HubSpot Use Case: Identify competitors and industry leaders
7. Cache: Operator
Purpose: View Google’s cached version Syntax: cache:domain.com/page Example: cache:example.com/blog-post shows the last cached version Use Case: See how Google indexes your pages or access unavailable content
File Type and Content Operators
8. Filetype: Operator
Purpose: Find specific file formats Syntax: filetype:extension search terms Example: filetype:pdf "marketing budget template" finds PDF templates Use Case: Discover downloadable resources, research reports, presentations
Popular File Types to Search:
filetype:pdf– Research reports, ebooks, guidesfiletype:ppt– Presentations and slide decksfiletype:xlsx– Spreadsheets and templatesfiletype:doc– Documents and proposals
9. Inurl: Operator
Purpose: Find pages with specific words in the URL Syntax: inurl:keyword search terms Example: inurl:blog marketing tips finds blog posts about marketing Use Case: Target specific page types or content categories
10. Intitle: Operator
Purpose: Find pages with specific words in titles Syntax: intitle:keyword Example: intitle:"SEO guide" finds pages with “SEO guide” in the title Use Case: Research content gaps or analyze title strategies
Advanced Search Operators for SEO and Marketing Professionals

Competitive Intelligence Operators
11. Intext: Operator
Purpose: Find specific text within page content Syntax: intext:keyword Example: intext:"powered by WordPress" marketing agency finds WordPress-powered marketing sites Use Case: Identify technology stacks or specific mentions
12. Allinurl: Operator
Purpose: Find pages with ALL specified words in URL Syntax: allinurl:word1 word2 Example: allinurl:digital marketing agency finds URLs containing all three words Use Case: Find specific service pages or content categories
13. Allintitle: Operator
Purpose: Find pages with ALL words in title Syntax: allintitle:word1 word2 Example: allintitle:local SEO guide finds titles containing all terms Use Case: Research content competition and gaps
Link Analysis Operators
14. Link: Operator (Deprecated but alternatives exist)
Purpose: Previously found pages linking to a site Current Alternative: Use "domain.com" -site:domain.com to find external mentions Example: "salesnanny.com" -site:salesnanny.com finds external mentions of SalesNanny Use Case: Find backlink opportunities and brand mentions
Technical SEO Operators
15. Info: Operator
Purpose: Get basic information about a webpage Syntax: info:domain.com Example: info:google.com shows Google’s information Use Case: Quick technical overview of any website
16. Define: Operator
Purpose: Get definitions of terms Syntax: define:term Example: define:conversion rate optimization Use Case: Research industry terminology and create glossaries
Location and Time-Based Operators
17. Location Targeting
Purpose: Find location-specific results Syntax: search terms location:city or search terms near:city Example: marketing agency location:Chicago Use Case: Local competitor research and market analysis
18. Date Range Searches
Purpose: Find content from specific time periods Method: Use Google’s Tools > Any time > Custom range Use Case: Find recent industry news, trending topics, or historical data
Practical Use Cases and Real-World Applications
For Content Marketers
1. Research Content Gaps
- Search:
allintitle:"your topic" site:competitor.com - Purpose: See what content competitors have created on your topic
- Action: Identify gaps in their coverage for your content strategy
2. Find Guest Posting Opportunities
- Search:
"guest post" OR "write for us" marketing - Purpose: Discover websites accepting guest contributions
- Action: Build your outreach list for guest blogging
3. Source Statistics and Data
- Search:
filetype:pdf "marketing statistics 2025" - Purpose: Find authoritative research reports
- Action: Gather data for your content with proper citations
For SEO Professionals
1. Competitor Backlink Research
- Search:
"competitor.com" -site:competitor.com - Purpose: Find sites mentioning your competitors
- Action: Reach out for similar coverage or partnerships
2. Technical Site Audits
- Search:
site:yoursite.com filetype:pdf - Purpose: Find all PDFs indexed on your site
- Action: Ensure proper optimization and internal linking
3. Index Coverage Analysis
- Search:
site:yoursite.com - Purpose: See how many pages Google has indexed
- Action: Compare with your expected page count and investigate gaps
For Business Researchers
1. Industry Analysis
- Search:
"industry report" filetype:pdf 2025 - Purpose: Find recent industry research
- Action: Stay updated on market trends and opportunities
2. Competitor Intelligence
- Search:
site:competitor.com "case study" OR "success story" - Purpose: Analyze competitor client work
- Action: Understand their positioning and service offerings
Advanced Operator Combinations
Power User Techniques
1. Multiple Operator Stacking
site:linkedin.com/in intitle:"marketing manager" location:New YorkPurpose: Find marketing managers in New York on LinkedIn
2. Content Research Formula
"how to" + your topic + filetype:pdfPurpose: Find comprehensive guides on any topic
3. Competitor Content Analysis
site:competitor.com intitle:"ultimate guide" OR intitle:"complete guide"Purpose: Find competitor’s pillar content
Operator Combinations Table
| Goal | Operator Combination | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Find expert roundups | "expert roundup" OR "experts weigh in" + your topic | "expert roundup" marketing trends |
| Discover broken links | site:yoursite.com "404" OR "page not found" | Find 404 errors on your site |
| Research presentations | filetype:ppt OR filetype:pptx + your topic | filetype:ppt "social media strategy" |
| Find email addresses | site:domain.com "@" OR "email" | Contact information research |
| Source infographics | filetype:jpg OR filetype:png intitle:infographic + topic | Visual content research |
Tools and Browser Extensions for Search Operators
Browser Extensions
- SearchOperators.com Extension: Quick access to operator syntax
- Google Search Shortcuts: Keyboard shortcuts for common operators
- Advanced Search Tool: GUI interface for complex operator combinations
Mobile Usage
Most search operators work on mobile Google search, though the interface may vary. For best results:
- Use Google app rather than browser
- Type operators manually (autocomplete may interfere)
- Save frequent operator searches as bookmarks
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting
Syntax Errors to Avoid
1. Spacing Issues
- ❌ Wrong:
site: domain.com - ✅ Correct:
site:domain.com
2. Quote Placement
- ❌ Wrong:
site:"domain.com" - ✅ Correct:
site:domain.com "search phrase"
3. Operator Case Sensitivity
- Most operators are case-insensitive
- File extensions in
filetype:should be lowercase
When Operators Don’t Work
Deprecated Operators:
link:operator was retired+operator largely replaced by quotes- Some operators may return limited results
Alternative Solutions:
- Use third-party SEO tools for comprehensive backlink analysis
- Combine multiple operators for better results
- Check Google’s official documentation for current operator status
Search Operators for Different Industries
E-commerce Businesses
site:competitor.com "product reviews"– Analyze competitor review strategiesfiletype:pdf "pricing guide" + industry– Research pricing strategiesintitle:"vs" + your product category– Find comparison content opportunities
B2B Services
site:linkedin.com "looking for" + your service– Find prospects actively seeking servicesfiletype:ppt + industry + "case study"– Discover client success stories"RFP" OR "request for proposal" + your expertise– Find business opportunities
Local Businesses
"best" + service + city + year– Research local competition rankingssite:yelp.com OR site:google.com/maps + business type + location– Monitor review mentions"[city] + business directory"– Find local listing opportunities
The Future of Google Search Operators
Current Trends (2025)
As these changes unfold, we’re seeing a rise in zero-click searches — instances where users either get the information they need directly from the SERP without clicking through to any site. This makes search operators even more valuable for finding specific, detailed information.
AI Impact on Search
With Google’s continued AI integration, search operators remain crucial for:
- Bypassing AI overviews when you need specific source material
- Finding technical information that AI summaries might oversimplify
- Conducting precise research that requires exact matches
Emerging Operator Uses
- Voice Search Compatibility: Some operators work with voice commands
- Mobile-First Indexing: Operators help verify mobile page indexing
- Core Web Vitals Research: Find technical performance discussions
Quick Reference Cheat Sheet
Most Important Operators (Top 10)
site:domain.com– Search within specific sites"exact phrase"– Find exact matches-unwanted– Exclude termsfiletype:pdf– Find specific file typesintitle:keyword– Search page titlesinurl:keyword– Search URLsrelated:domain.com– Find similar sitescache:url– View cached pagesdefine:term– Get definitions* wildcard– Replace unknown words
Operator Categories by Use Case
- Content Research:
intitle:,"exact phrase",filetype: - Competitor Analysis:
site:,related:, external mention searches - Technical SEO:
cache:,info:,site:for indexing - Link Building: External mention searches, guest post opportunities
- Market Research:
filetype:pdf, date ranges, industry terms
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Do all Google search operators still work in 2025?
Google is continually working on new things and discarding old projects. Don’t expect the list above to stay the same for very long. They typically retire their rarely-used search operators with little warning. While most core operators still function, some have been deprecated. Always test operators periodically and have backup methods ready.
Q2: Can I use multiple search operators in one query?
Yes, you can combine multiple operators for more precise results. For example: site:competitor.com intitle:"marketing" filetype:pdf finds PDF files about marketing on a competitor’s site. However, too many operators may limit results significantly.
Q3: Why do some search operators return fewer results than expected?
Search operators work within Google’s index limitations. Factors affecting results include:
- Recent algorithm updates
- Site crawling issues
- Geographic restrictions
- Personalized search settings
Clear your search history and use incognito mode for more consistent results.
Q4: Are Google search operators useful for voice search?
While most operators work better with typed queries, some basic operators like “site:” can be used with voice commands. However, complex operator combinations are still best performed through traditional text search.
Q5: How often should I use search operators for SEO research?
For active SEO monitoring, use operators:
- Weekly: Monitor brand mentions and competitor content
- Monthly: Analyze site indexing and technical issues
- Quarterly: Conduct comprehensive competitive research
- As needed: For specific research projects and content creation
Q6: Can search operators help with local SEO?
Absolutely. Operators like site:google.com/maps + business name help monitor local listings, while location-based searches can reveal local competitor strategies and directory opportunities.
Q7: Do search operators work the same way in different countries?
Most operators work globally, but results may vary based on:
- Local Google domains (.com, .co.uk, .ca)
- Language and region settings
- Local content indexing priorities
For international research, specify your target country’s Google domain.
Conclusion: Mastering Search Operators for Better Results
Google search operators transform casual searching into precision research. Whether you’re analyzing competitors, researching content opportunities, or conducting technical SEO audits, these commands provide insights that would otherwise require expensive tools or hours of manual work.
The key to mastering search operators is consistent practice. Start with the top 10 operators from our cheat sheet, then gradually incorporate more advanced combinations as you become comfortable with the syntax.
Remember that effective organic marketing strategies often depend on thorough research – and search operators are among your most powerful research tools. They help you understand your competitive landscape, identify content opportunities, and discover technical insights that can significantly improve your digital marketing efforts.
Your next step: Choose three operators from this guide that align with your immediate needs. Practice using them this week, and gradually build your operator vocabulary.
Which search operator will you try first, and what specific challenge are you hoping to solve with it?








Leave a Comment
Surya Prakash
Hi, I’m Surya Prakash — a digital marketing strategist. I help startups and digital-first brands grow online using a mix of SEO, AEO, content marketing, and brand storytelling. You can follow my blog insights here, where I break down complex marketing topics into simple, useful ideas.
Comments
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!